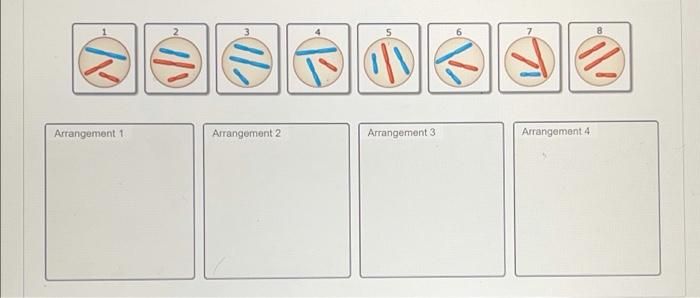
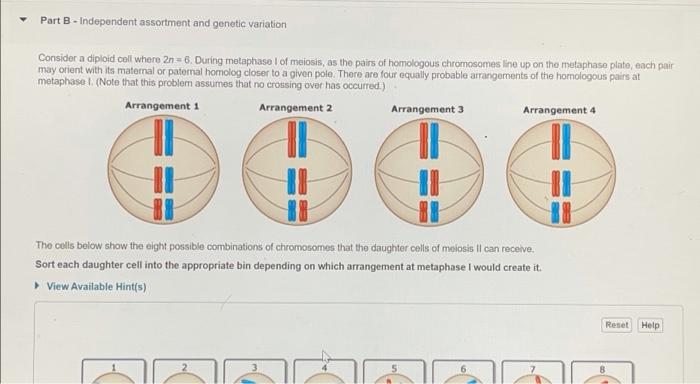
Part B Independent Assortment and Genetic Variation
There are four equally probable arrangements of the homologous pairs at. When cells divide during meiosis homologous chromosomes are randomly distributed to daughter cells and different chromosomes segregate independently of each other.
Solved Part B Independent Assortment And Genetic Variation Chegg Com
During metaphase 1 of meiosis as the pairs of homologous chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate each pair may orient with its maternal or paternal homolog closer to a given pole.
. Hence when you produce gametes your genes are scrambled in each. Independent assortment occurs when paired homologous are separated into daughter cells during meiosis. In the 2019 exam paper question 3 part b it asks you to explain how sexual reproduction of kauri trees causes genetic variation.
We have option number A which stays so option number is says that independent assortment of non homologous chromosome creates different combination of police among the chromosomes. Random crossing over results in different combinations of genes that may segregate into the gametes. Not surprisingly the principle of independent assortment applies to the definition of.
This process adds to the genetic variation in the offspring and hence the correct option over yours. Arrangement 1- 3 and 8 Arrangement 2- 1 and 5 Arrangement 3- 6 and 2 Arrangement 4- 4 and 7. Meiosis can result in genetic variation for random fertilisation mutation crossing over between the chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
AlL BUT ONE applies to meiosis and genetic variation. It is important to understand how crossing over occurs and its consequences in meiosis. Crossing over the exchange and recombination of genetic information between chromosomes also occurs in prophase I and adds to the genetic diversity of the offspring.
Mendels law of independent assortment states that the alleles of two or more different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. PART B Crossing over. Genetic variation results from independent assortment because it results in.
This option is incorrect. There are four equally probable. Genetic variation only- NONE.
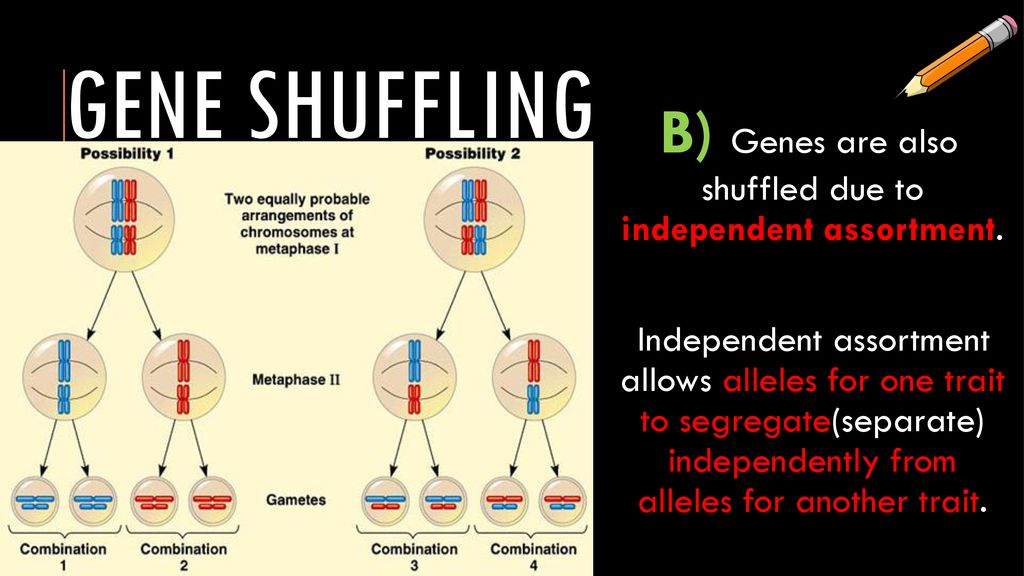
I Independent Assortment. It results in new combinations of genes on each chromosome. This variation allows for genetic differentiation in offspring.
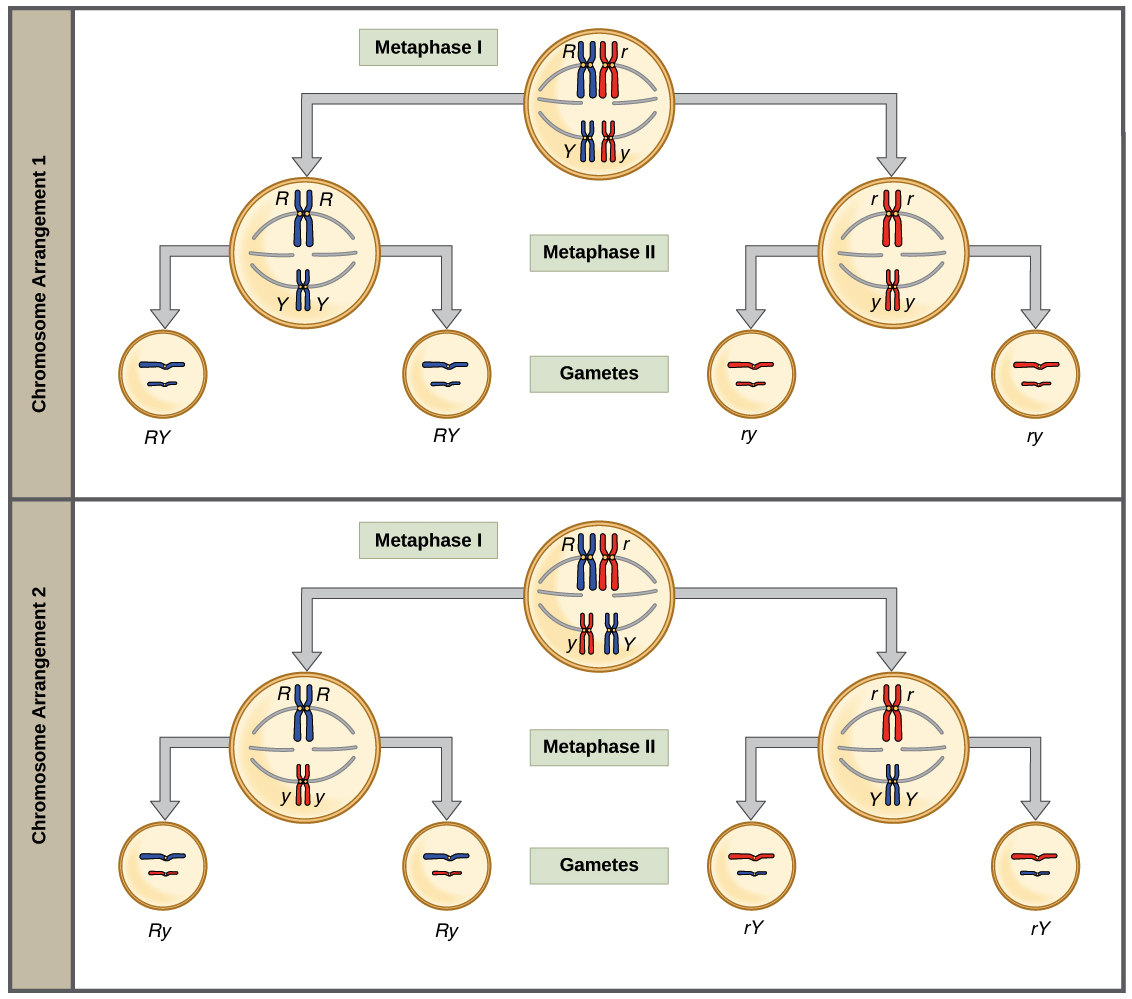
During meiosis independent eg. D only one of the two alleles for a trait is passed to offspring. Independent assortment is achieved when chromosomes line up in homologous pairs and move independently to the one pole or the other.
The Principle of Independent Assortment. Crossing-over is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. A law of segregation B independent assortment replication of chromosomes D recombination due to crossing over.
Consider how the. Part B Independent assortment and genetic variation Consider a d loid cell where 2n 6 During metaphase of meiosis as he pairs of homologous chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate each pair may or ent with its matemal or paternal homolog closer to a given pole. The possible variation that can be achieved by independent assortment depends.
The process is governed by complex enzyme systems which in turn must also have come about by chance. B recombination of chromosomes during crossing over. Here you would talk about either independent assortment OR crossing over.
Student Science Performance Grade. Meiosis and sexual reproduction are in large part responsible for genetic variation within a population. This phenomenon is called independent assortment.
Independent assortment is a genetic term that refers to the variation of chromosomes or genetic information during sex cell division. This called is called independent. Independent Assortment Definition.
C replication of chromosomes at the beginning of the process. The law of independent assortment states that the alleles for a trait separate when gametes are. All BUT ONE applies to meiosis and genetic variation.
Part C- Assume that an organism exists in which crossing over does not occur but that all other processes associated with meiosis occur normally. Like segregation independent assortment occurs during meiosis specifically in prophase I when the chromosomes line up in random orientation along the metaphase plate. Dec 6 2017.
If you read the mark schedule you will see you that They arent explained in a lot of depth. The general basis for the law of independent assortment remains in the stage of meiosis 1 of gamete formation when homologous pairs are lined up in a not-so-obvious orientation at the center of the cell as they prepare to part. In other words the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene.
Mendel formulated this principle after discovering another principle known as Mendels law of segregation both of which govern heredity. Meiosis supports genetic variation in several ways. Moreover since it is only half a complement of your chromosomes this leaves room for more genetic diversity when you mate with.
In conclusion crossing over and independent assortment sometimes called random assortment are different independent processes that both lead to an increase in genetic diversity. Independent assortment is a basic principle of genetics developed by a monk named Gregor Mendel in the 1860s. A independent assortment of chromosomes.
Crossing over plays a critical role in increasing the genetic variation among offspring of sexual reproduction. Meiosis supports genetic variation in several ways. Independent assortment increases genetic variation by allowing daughter cells to each randomly receive a different proportion of paternal and maternal chromosomes.
Look carefully at the diagrams depicting different stages in meiosis in a cell where 2n 6. Part B - Independent assortment and genetic variation. Humans have 23 chromosomes so this gives rise to 8388608 genetically unique gametes through independent assortment alone Random fertilization refers to the fact that if two individuals mate and each is capable of producing over 8million potential gametes the random chance of any one sperm and egg coming together is a product of these two probabilities -.
The chromosomes are lined up in the center of the cell and are then pulled to opposite sides. Patterns in Heredity Selection--Mendelian Genetics Part 1 of 2 This 5E model for instruction may be useful in connecting the concepts of meiosis with chromosomal mutations due to errors in meiosis before transitioning to Mendels Law of Independent Assortment and dihybrid crosses. Part B - Independent assortment and genetic variation Consider a diploid call where 2n 6.

Mastering Ch 13 Flashcards Quizlet
Do Now Activity 4 What Is The Difference Between Co Dominance And Incomplete Dominance What Is The Difference Between A Mono Hybrid Punnet Square Ppt Download

What Is Crispr How Could It Edit Your Dna Medical Tech Integrative Medicine Internet Technology
The Law Of Independent Assortment Article Khan Academy

Mastering Ch 13 Flashcards Quizlet

Mastering Ch 13 Flashcards Quizlet

Mastering Biology Ch 13 Homework Flashcards Quizlet

4 Worksheet Dominant Recessive Genes Life Science A Dominant Trait Is The Allele That Will Ap Science Biology Genetics Lesson Biology Classroom

The Process Of Meiosis And How Genetic Variation Is Achieved Through Crossing Over And Random Independent Assortment Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis Genetic Variation

Mastering Ch 13 Flashcards Quizlet
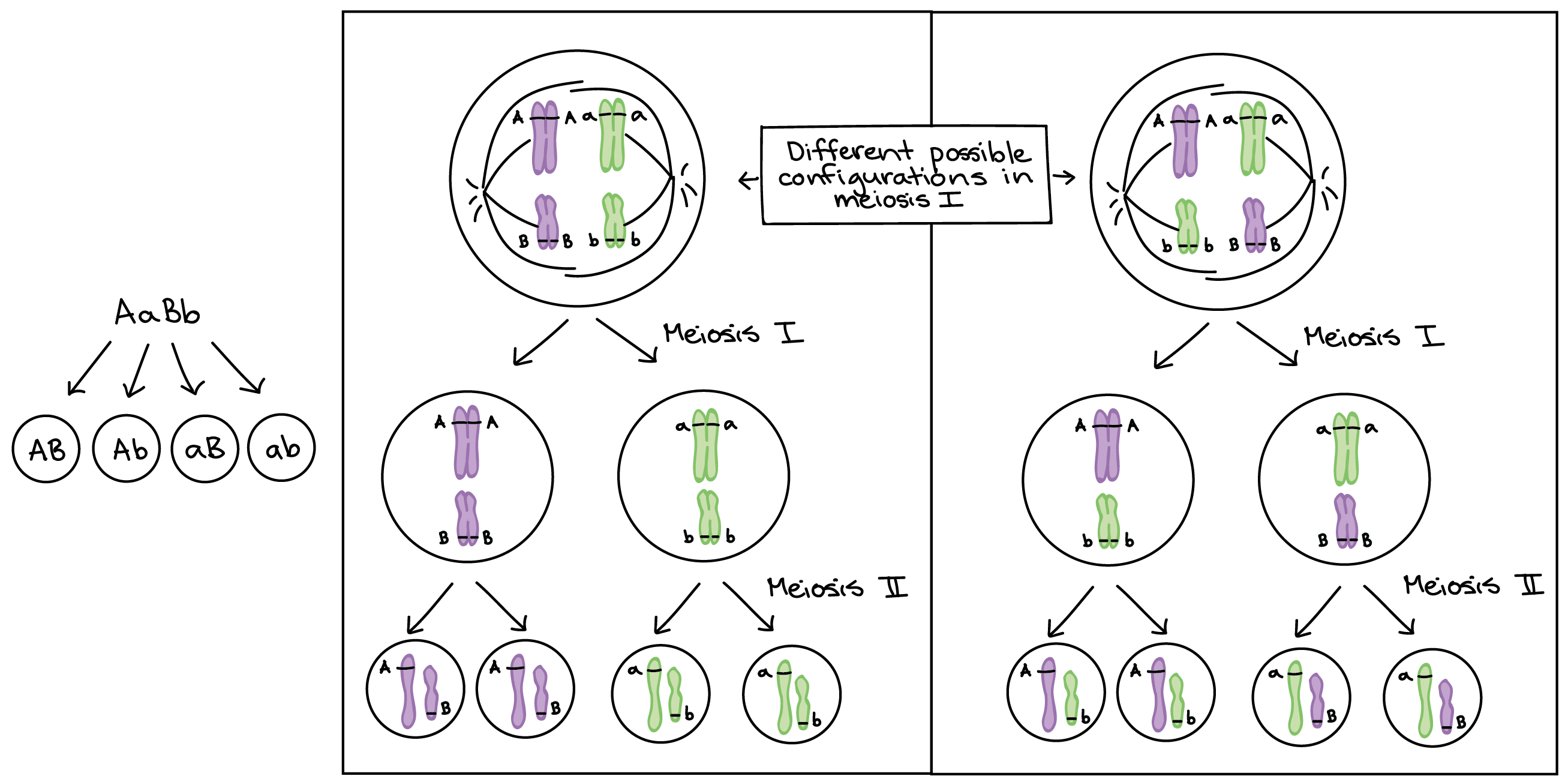
The Chromosomal Basis Of Inheritance Article Khan Academy

Solved Part B Independent Assortment And Genetic Variation Chegg Com

Mastering Ch 13 Flashcards Quizlet

Solved Part B Independent Assortment And Genetic Variation Chegg Com
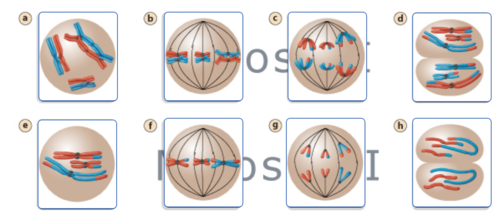
Mastering Ch 13 Flashcards Quizlet

Phylogenetic Relationships Of The N2 Na A And N8 Na B Genes Of Aivs Download Scientific Diagram

Genetic Recombination An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
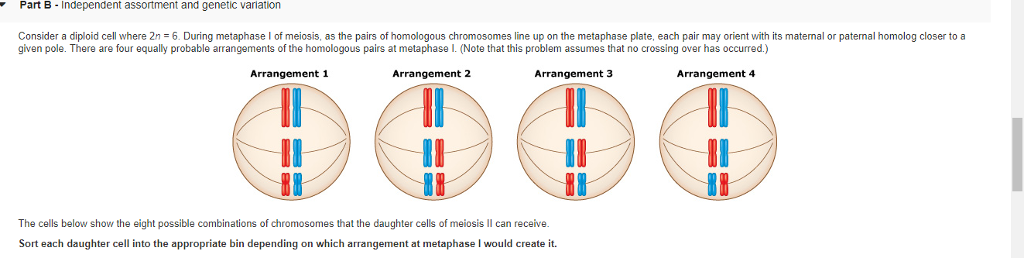
Solved Part B Independent Assortment And Genetic Variation Chegg Com

Comments
Post a Comment